Overview:
Where is Algeria heading in 2025?
From GDP growth and inflation to population trends and income shifts— this report dives deep into the key factors shaping Algeria’s economic and demographic landscape.
Explore the full analysis now and stay ahead of the curve.
Algeria Gross domestic product (GDP) 2019-2027

After a significant dip in 2020 due to the global pandemic and oil market disruptions, Algeria’s GDP has shown a strong recovery, rising from $164.8 billion in 2020 to an estimated $265.05 billion in 2024. Projections through 2027 suggest continued, albeit moderate, growth — reaching $310.2 billion. This upward trend reflects improved energy revenues, public investment initiatives, and gradual economic diversification efforts. Maintaining momentum will depend on structural reforms and stability in global energy markets.
Algeria Consumer Price Index (CPI) 2018-2024

Algeria’s Consumer Price Index has steadily increased from 202.25 in 2018 to an estimated 281.43 in 2024, reflecting persistent inflationary pressures over the past six years. The sharpest upticks occurred post-2020, driven by global supply chain disruptions, rising import costs, and domestic monetary dynamics. The CPI jumped by over 10% in both 2021 and 2022, signaling a period of heightened cost-of-living concerns. While the rate of increase appears to be moderating slightly in 2024, inflation remains a key economic challenge, impacting household purchasing power and fiscal planning.
Algeria Inflation Rate 2019-2024:

Algeria’s inflation rate remained relatively moderate between 2019 and 2020, averaging around 2–3%. However, starting in 2021, inflation accelerated sharply — peaking at 9.37% in 2023 — fueled by global price shocks, increased food and energy costs, and local supply constraints. In 2024, inflation is projected to ease slightly to 6.62%, though it remains well above pre-2021 levels. This volatility underscores the need for targeted monetary policies and stronger domestic production to curb imported inflation and stabilize consumer prices.
Algeria Interest Rates 2017-2024:

Algeria’s interest rates have remained largely stable between 3% and 3.5% from 2017 to 2024, reflecting a cautious monetary policy aimed at maintaining economic stability. Despite external and domestic economic pressures, including fluctuations in oil prices and inflationary challenges, the central bank has kept rates relatively unchanged, signaling an effort to foster investment and maintain credit accessibility. The consistent rate of 3% since 2020 indicates a policy stance focused on controlling inflation while supporting economic recovery post-pandemic.
Algeria Trade Balance 2018-2025:
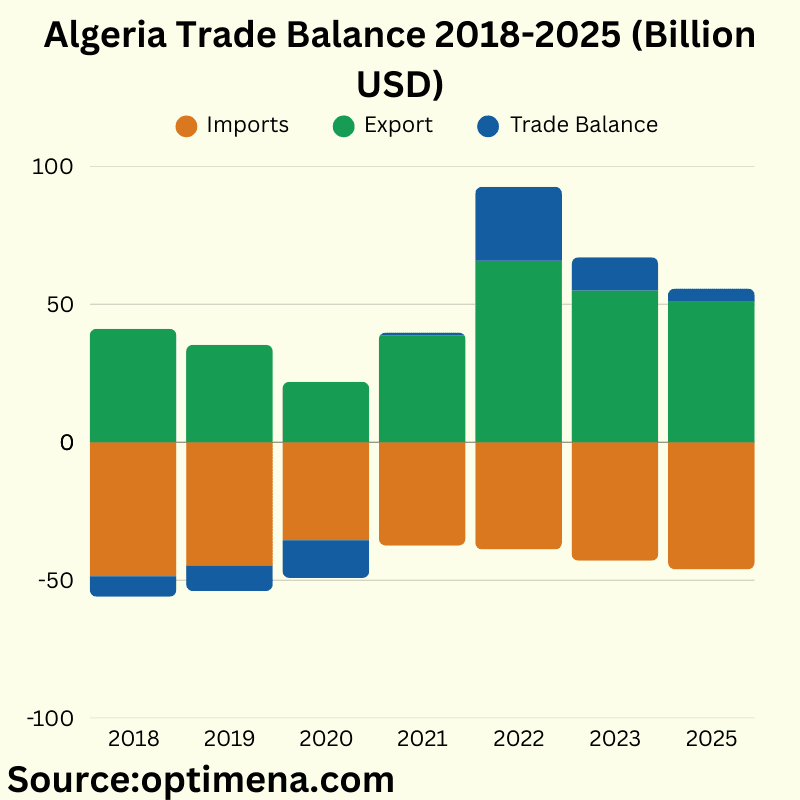
Annual Trade Balance Results (2018–2025, USD Billion)
2018
– Trade Balance: -7.4
– Exports: 41.1
– Imports: 48.6
2019
– Trade Balance: -9.3
– Exports: 35.3
– Imports: 44.6
2020
– Trade Balance: -13.6
– Exports: 21.9
– Imports: 35.5
2021
– Trade Balance: +1.2
– Exports: 38.6
– Imports: 37.5
2022
– Trade Balance: +26.9
– Exports: 65.7
– Imports: 38.9
2023
– Trade Balance: +12.0
– Exports: 55.0
– Imports: 43.0
2025 (Projected)
– Trade Balance: +4.8
– Exports: 50.9
– Imports: 46.1
Algeria’s trade balance swung from deep deficits (-$13.6B in 2020) to record surpluses (+$26.9B in 2022), reflecting extreme sensitivity to hydrocarbon prices and global shocks (e.g., COVID-19 in 2020, Russia-Ukraine conflict in 2022).
– 2018–2020: Deficits widened as oil/gas exports collapsed (-47% in 2020), while imports remained elevated.
– 2021–2022: Post-pandemic energy price surges (+200% exports in 2022) reversed the trend, showcasing reliance on hydrocarbons.
– 2023–2025: Projected surplus erosion aligns with moderating energy prices and OPEC+ supply limits.
– Imports fell sharply in 2020 (-23% YoY) due to economic contraction but rebounded steadily post-2021, reaching $46.1B by 2025 (projected). This suggests rising domestic demand and inflationary risks.
Algeria’s trade balance remains tied to volatile energy markets. While short-term surpluses (2021–2023) offer fiscal relief, long-term stability depends on reducing hydrocarbon reliance and boosting non-oil exports.
Algeria Foreign Exchange Reserves 2019-2027 :

2019
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $ 65.75 B
2020
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $48.16B
2021
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $45.29B
2022
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $60.99B
2023
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $68.98B
2024
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $72.00B
2025
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $72.95B
2026
-Foreign Exchange Reserves: $72.41B
2027
– Foreign Exchange Reserves: $72.36 B
– Foreign exchange reserves plummeted by 31% from 2019 to 2021 (65.75B → 45.29B), reflecting Algeria’s heavy reliance on hydrocarbon exports. The 2020 crash (-27% YoY) coincided with COVID-19-driven oil price collapses ($60/barrel in 2019 → $40 in 2020).
– Reserves rebounded sharply by 52% from 2021 to 2023 (45.29B → 68.98B), driven by surging global energy prices post-Russia-Ukraine conflict. Algeria leveraged its role as a key gas supplier to Europe, boosting export revenues.
– Foreign exchange reserves are expected to stabilize near $72B, peaking at 72.95B in 2025 before marginal declines to 72.36B by 2027. This suggests prudent fiscal management to preserve reserves amid moderating energy prices and global uncertainty.
Algeria Demographics Outlook:
Algeria Population 2018-2025

Algeria’s population grew steadily from 41.9 million in 2018 to 47.4 million in 2025, reflecting an annual growth rate decline from 1.9% to 1.5%.
– Growth rates gradually eased (1.9% → 1.5%) due to declining fertility, urbanization, and delayed marriages, aligning with regional demographic transitions.
– Total increase: +5.5 million people** (13% rise over 7 years).
Population growth is projected to stabilize near 1.5% by 2025, emphasizing the need for policies balancing youth empowerment and aging preparedness.
Algeria population by age distribution:

Algeria’s age structure highlights both opportunities (a large workforce) and risks (youth unemployment, aging pressures). Strategic planning is critical to harness its demographic potential
1.Youthful Population:
– Children (0–14 years): ~13.2 million, accounting for 28.5% of the total population.
– Largest cohorts: 5–9 years (5.0 million) and 10–14 years (4.3 million), reflecting high birth rates in the 2000s–2010s.
-Adolescents (15–24 years): ~6.4 million (**13.8%** of population), with a noticeable dip in the 20–24 group (2.9 million), suggesting declining fertility rates post-2000.
2.Working-Age Majority (25–59 years):
– ~16.9 million (36.5% of population), peaking in the 35–39 group (3.76 million).
– This segment forms the core labor force but faces pressure to absorb youth entering the job market.
- Aging Population:
– 60+ years: ~4.5 million (9.7%), with a steep decline after age 75.
– Limited elderly care infrastructure, as only 1.2 million are aged 70+ (2.6% of total).
– Youth Bulge: A large child/adolescent population signals potential for a future “demographic dividend” but requires heavy investment in education, healthcare, and job creation.
– Declining Fertility: Smaller cohorts in younger age groups (e.g., 0-year-olds: 884K vs. 5–9: 5.0M) suggest falling birth rates, aligning with regional trends of urbanization and delayed marriage.
– Aging Pressures: While still young overall, the growing 60+ population (~9.7%) will strain pensions and healthcare systems in the coming decades.
Algeria Average Income :

From 2018 to 2021, Algeria’s average monthly income in DZD showed modest growth — rising from 40,955 DZD to 42,848 DZD. However, when adjusted to USD, income steadily declined from $350.94 to $317.15, mainly due to currency depreciation. This divergence highlights the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on real purchasing power, especially for imported goods and international spending.






